SMTP Smuggling: Overview
The landscape of cybersecurity is evolving, so modern threats like SMTP smuggling are a stark reminder of the importance of staying up to date on defending against such cyberattacks. But what is SMTP smuggling, how does it work?
What is Simple Mail Transfer Protocol?
Simple Mail Transfer Protocol is a TCP/IP network protocol utilized to send emails between different servers. SMTP email clients include Gmail, Outlook, Yahoo, etc.
Basically, after an email is composed, using a client such as Gmail or Outlook, it is delivered to an SMTP server, which verifies the recipient’s domain to find the appropriate email server to deliver the email to. The SMTP server at the recipient’s domain processes the email, and either delivers the message or uses SMTP to forward it via another network before delivery.
What is SMTP Smuggling?
Security is the biggest problem with the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol because it lacks authentication. With the right tools, hackers can simply choose the sender’s name, so that their messages appear to have been sent from legitimate sources. They try to convince the recipients to take specific actions, such as clicking phishing links, downloading files infected with malware, sending sensitive information, etc.
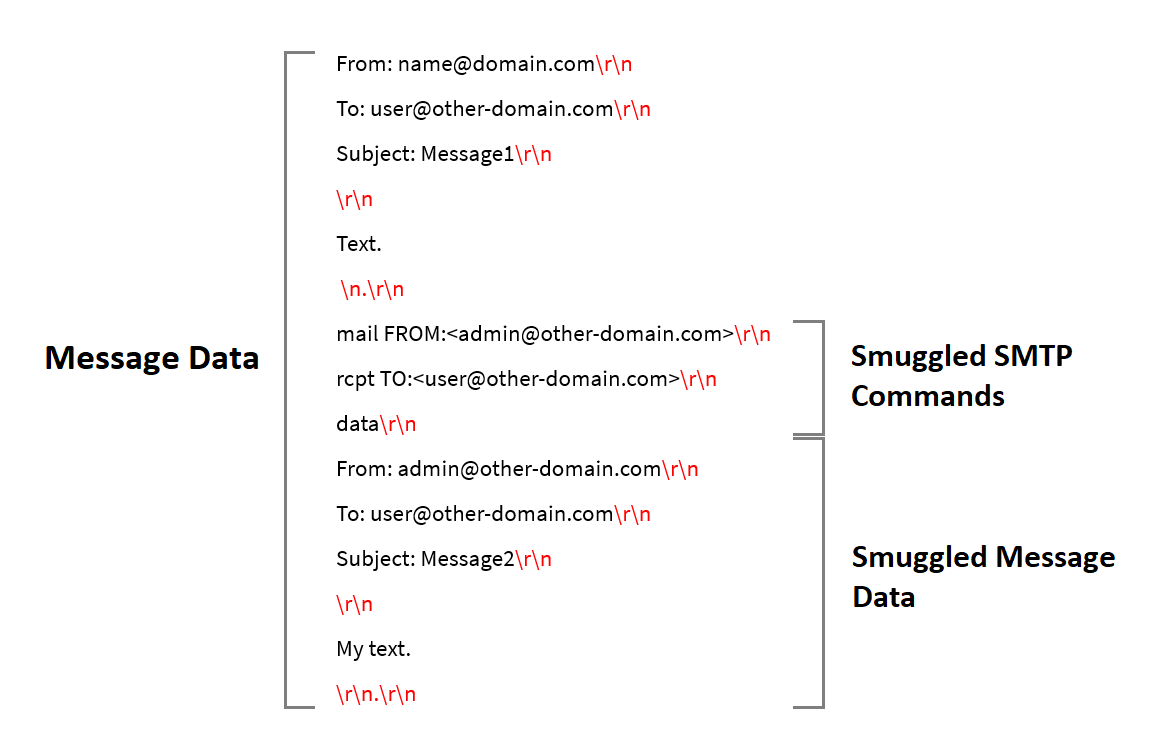
The goal is to trick the recipient’s server into a different interpretation of the end of a message using SMTP commands so that the email appears as two separate messages.
How Does SMTP Smuggling Work?
To perform such attacks, hackers “smuggle” ambiguous SMTP commands to eventually compromise the integrity of the email-server communications. Basically, SMTP servers usually indicate the end of message data with the code <CR><LF> also known as “Carriage Return” and “Line Feed” or “\r\n.\r\n”. These are the standard text delimiters.
By changing this code sequence, hackers can alter the server’s understanding of where the message data ends. This creates an opportunity for smuggling extra data.
Spoofed emails are usually just a part of targeted phishing attacks. Organizations are particularly vulnerable to SMTP smuggling because it can be easy to spoof their domains and use social engineering to send phishing emails or launch spear-phishing attacks.
How to Avoid SMTP Smuggling Emails
Manufacturing companies of the most popular mail servers, such as Postfix, Exim, and Sendmail have released solutions to defend against SMTP smuggling. Several other measures can be taken to minimize the threat.
We strongly advise running regular IT security checks on your organization’s infrastructure to monitor possible attack vectors and vulnerabilities.
Check the email-routing software being used. If the software is known to be vulnerable, update it to the latest version and use settings that specifically reject unauthorized additions.
Conduct security awareness training regularly, teach employees how important it is to always verify the sender’s email address and full name before proceeding with any actions.
What Does SMTP Email Spoofing Look Like?
To be alert to the threat of SMTP smuggling, it is critical to know what a spoof email might look like. A spoof email may take several forms.
There is the case of display name spoofing, where the sender’s name is spoofed, most times by using the real name of an organization’s employee. Most email clients automatically hide the sender’s email address and show the full name next to “From:”, which is why recipients should always check the email address to make sure it corresponds to the sender’s name to prevent downloading suspicious attachments, clicking links, or replying to deceitful emails.
Lookalike domain spoofing is a more complex cyberattack because it requires the perpetrator to register a domain like that of the target organization, set up the e-mail service, etc. There are two similar approaches that hackers take to domain spoofing: a misspelling of a legitimate company domain and Unicode Spoofing, where hackers replace an ASCII character in the domain name with a similar-looking character from Unicode.
At StratusPointIT we help organizations defend against various types of cyber threats, such as spoofing attacks. For more relevant information, or for a cybersecurity audit, please reach out to us.



